What Is A Flush Draw In Poker
- What Is A Flush Draw In Poker Room
- What Is A Nut Flush Draw In Poker
- What Is A Flush Draw In Poker Machines

You have quite a strong combo flush/open ended straight draw, but you have no overcards. Hitting an 8 or 7 is no good. You have to hit a heart or a 5 or a 10. A much stronger draw would be Q J on T 9 2 On that board, you have an open-ended straight flush draw with two overcards. Hitting a queen or jack might also be enough to win.
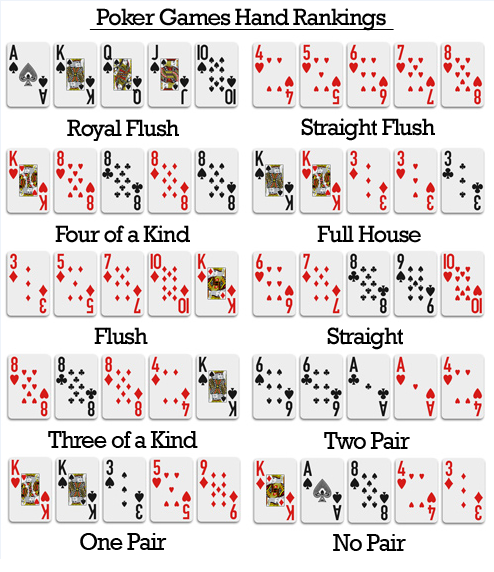
Flush Draw – A drawing hand which contains four of the five cards necessary to complete a flush.- An ace-high straight flush, commonly known as a royal flush, is the best possible hand in many variants of poker. Each hand belongs to a category determined by the patterns formed by its cards. A hand in a higher-ranking category always ranks higher than a hand in a lower-ranking category.
- With 2 suited cards, the probability of:. Flopping a flush - 118/1. Flopping a flush draw - 8.1/1. Flopping a backdoor flush draw - 1.4/1. Making a flush by the river - 15/1.
- (Redirected from Flush (poker)) An ace-high straight flush, commonly known as a royal flush, is the best possible hand in many variants of poker. In poker, players form sets of five playing cards, called hands, according to the rules of the game.
- Flush A Flush is a poker hand made out of five cards, all of which have the same symbol or suit. They are one of the mid-range poker hands as far as strength goes but it can still win a nice pot.
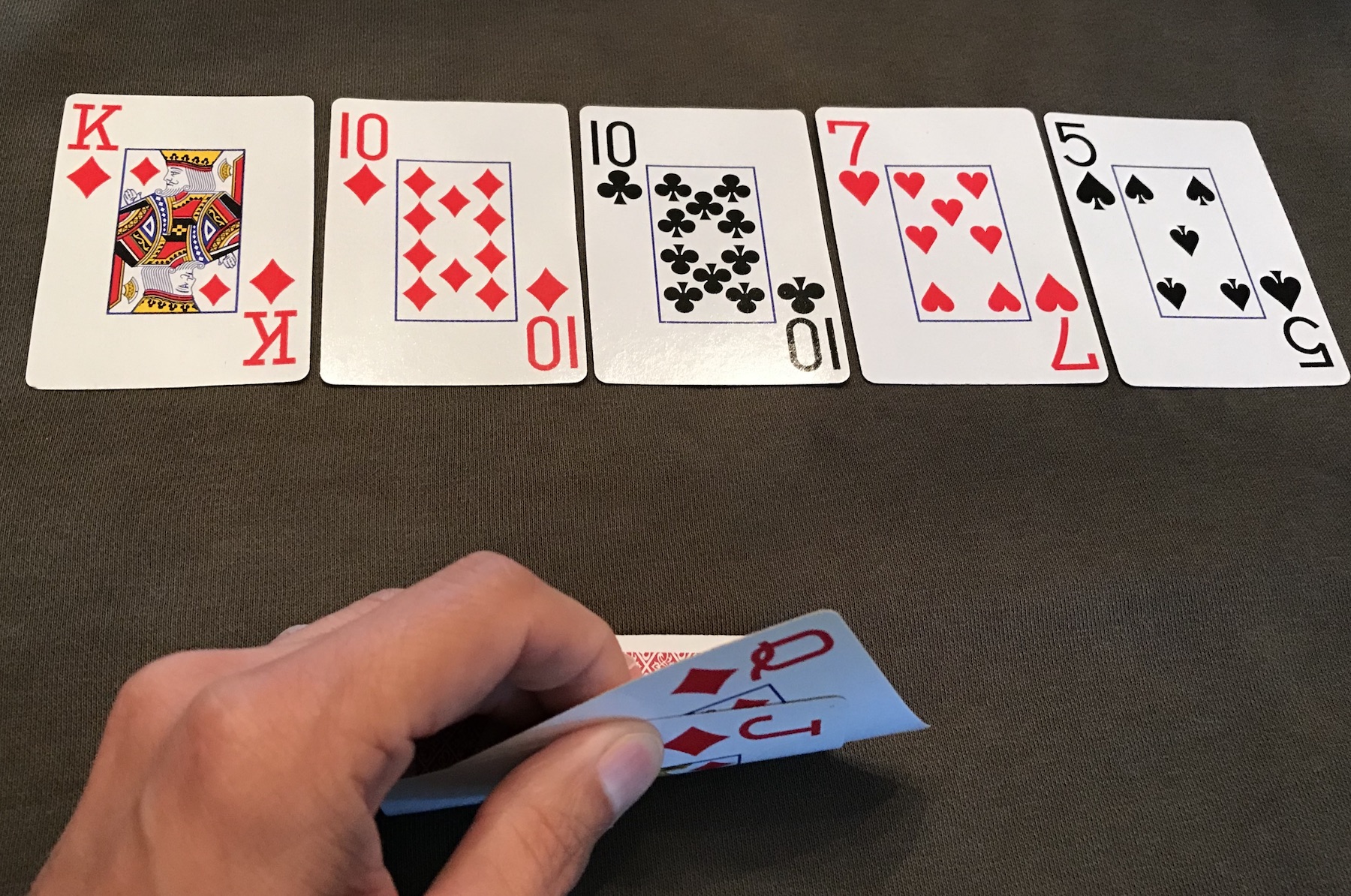
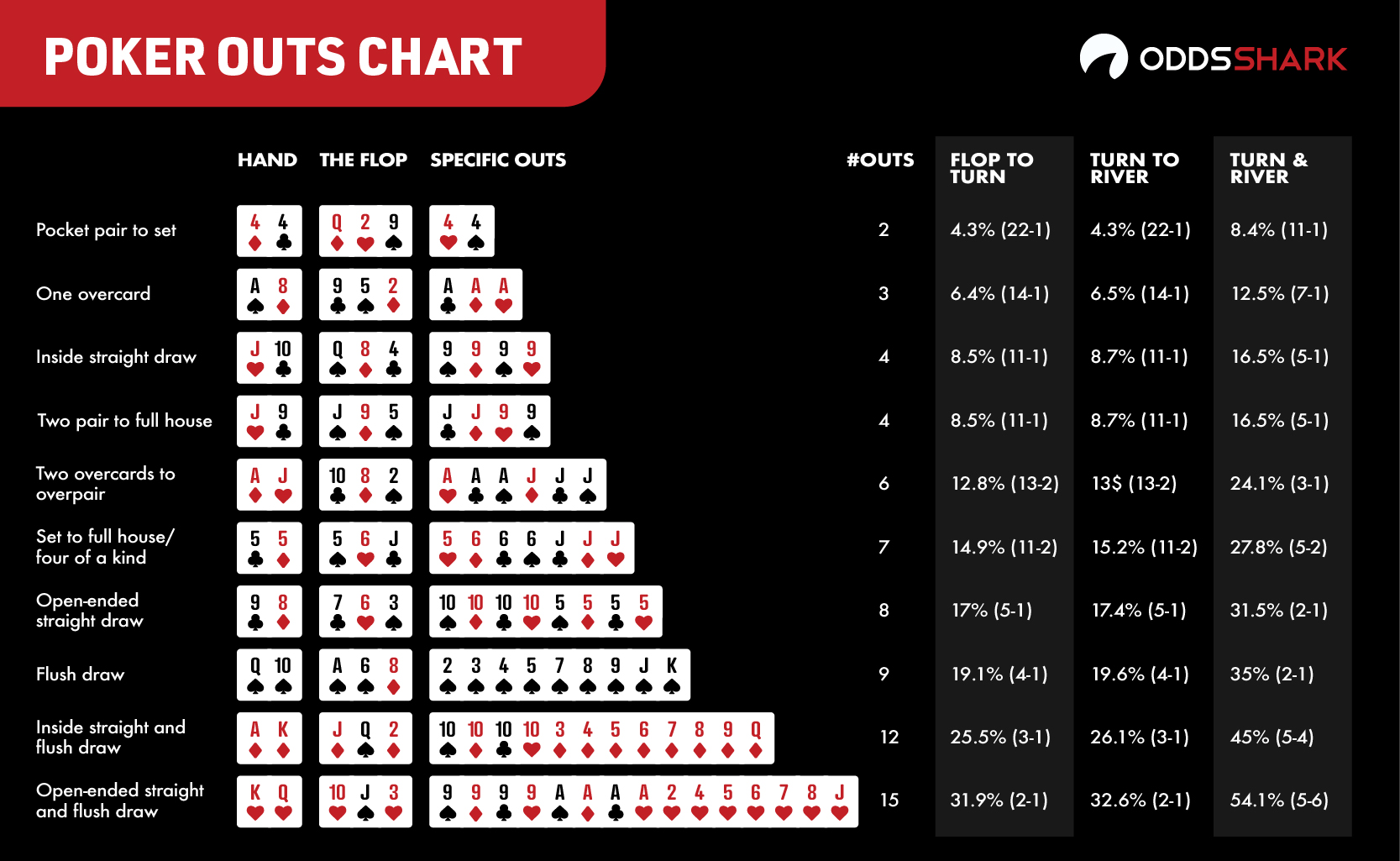 In most poker games, a valid poker hand must contain five cards. A flush consists of five cards of the same suit. If a player has only four cards of a particular suit, it adds no value to their hand at showdown. They must catch a fifth suited card in order to complete their flush. When a player holds four cards to a flush, and there are still cards left to come, he holds a flush draw. If the final card comes and he does not complete his flush, he now holds a busted flush draw.
In most poker games, a valid poker hand must contain five cards. A flush consists of five cards of the same suit. If a player has only four cards of a particular suit, it adds no value to their hand at showdown. They must catch a fifth suited card in order to complete their flush. When a player holds four cards to a flush, and there are still cards left to come, he holds a flush draw. If the final card comes and he does not complete his flush, he now holds a busted flush draw.The most powerful hand you can make in most poker games is a straight flush. This consists of five suited cards which are also in perfect sequence, for instance Q♠ J ♠ T ♠ 9 ♠ 8 ♠. A player who holds four of the five cards necessary to complete a straight flush holds a straight flush draw. When a straight flush is not possible, an ace high flush draw is the best possible flush draw. Depending upon the type of poker game you are in, you may hear an ace high flush draw referred to as a nut flush draw. A flush draw consisting of four low ranking cards is sometimes called a baby flush draw.
A flush draw can be a very powerful draw in a variety of different poker games, including Hold’em, Stud, and Omaha. If you complete one, a flush can be a very strong hand. The only hands that beat it are a higher flush, a full house, four of a kind, or a straight flush. However, if you fail to complete your flush, you are often left with a very weak hand. Since suited cards are necessarily unpaired, when you hold four of them and miss your flush, you may have only high cards to play.
This leads to a sense of anticipation when a player is on a flush draw. The situation is often clear. If you complete your flush draw you will likely win the pot. If you fail to complete it, you usually will not win the pot. That does not necessarily mean you should give up just because you have missed your flush draw. Depending upon the situation, if you have been betting your draw the whole way, it sometimes makes since to fire one more bet at the pot on the river, to try to take it down by bluffing. You don’t have to be successful very often for this play to be profitable.
Remember, the decision to bluff in this spot is made after all of the money is already in the pot. This decision should be made based upon a proper analysis of pot odds, implied odds, or preferably, both. If you divide the amount of the pot by your river bet, you can find out how often you need to successfully pull off the bluff in order to make it a profitable play. For example, if there were $60 in the pot, and it cost you $6 to try to bluff on the river, you would have to win, on average, at least one pot out of ten to make bluffing profitable over the long run. Here is why. If you consider that it costs $6 to try to bluff, you can also say that it costs $60 to try to bluff ten times. If you are successful on one of those occasions, you will receive the $60 that was in the pot, plus your $6 river bet. This represents a $66 return for your $60 investment. Given these inputs, the bluff play is clearly profitable and worth making. Anything better than a ten percent long term success rate increases the play’s profitability. Anything less than a ten percent success rate makes the bluff play unprofitable and not worth making. As you can see, you should sometimes bluff when you hold a busted flush draw, even if you don’t think that you are very likely to get away with it. It can also benefit you to show a bluff from time to time. If your opponents know that you are capable of it, it will force them to pay you off with a wider variety of hands. In other words, getting caught bluffing gets you paid off when you do actually have a hand.
Usage: Nut Flush Draw, Runner Runner Flush Draw, Baby Flush Draw
Mathematics: Flushes & Straights : Simple Pot Odds : Implied Odds : Reverse Implied Odds
Watch SplitSuit's video on Flushes and Flush Draws for 8 hand histories involving strategy on playing flushes in Texas Hold'em.
You are on the flop with a pretty decent flush draw. You have two hearts in your hand and there are another two on the flop.
Unfortunately, some cool cat has made a bet, putting you in a tricky situation where you have to decide whether or not it is in your best interest to call to try and make the flush, or fold and save your money.
This is a prime example of where you are going to take advantage of 'pot odds' to work out whether or not it is worth making the call.
What are pot odds? What about flushes and straights?
Basically, just forget about the name if you haven't heard about it before, there's no need to let it throw you off. Just think of 'pot odds' as the method for finding out whether chasing after a draw (like a flush or straight) is going to be profitable. If you're on your toes, you might have already been able to guess that it is generally better to chase after a draw when the bet is small rather than large, but we'll get to that in a minute...
Pot odds will tell you whether or not to call certain sized bets to try and complete your flush or straight draw.
Why use pot odds?
Because it makes you money, of course.
If you always know whether the best option is to fold or call when you're stuck with a hand like a flush draw, you are going to be saving (and winning) yourself money in the long run. On top of that, pot odds are pretty simple to work out when you get the hang of it, so it will only take a split second to work out if you should call or fold the next time you're in a sticky drawing situation. How nice is that?
How to work out whether or not to call with a flush or straight draw.
Now, this is the meat of the article. But trust me on this one, the 'working-out' part is not as difficult as you might think, so give me a chance to explain it to you before you decide to knock it on the head. So here we go...
Essentially, there are two quick and easy parts to working out pot odds. The first is to work out how likely it is that you will make your flush or straight (or whatever the hell you are chasing after), and the second is to compare the size of the bet that you are facing with the size of the pot. Then we use a little bit of mathematical magic to figure out if we should make the call.
1] Find out how likely it is to complete your draw (e.g. completing a flush draw).
All we have to do for this part is work out how many cards we have not seen, and then figure out how many of these unknown cards could make our draw and how many could not.
We can then put these numbers together to get a pretty useful ratio. So, for example, if we have a diamond flush draw on the flop we can work out...
The maths.
There are 47 cards that we do not know about (52 minus the 2 cards we have and minus the 3 cards on the flop).
- 9 of these unknown cards could complete our flush (13 diamonds in total minus 2 diamonds in our hand and the 2 diamonds on the flop).
- The other 38 cards will not complete our flush (47 unknown cards, minus the helpful 9 cards results in 38 useless ones).
- This gives us a ratio of 38:9, or scaled down... roughly 4:1.
So, at the end of all that nonsense we came out with a ratio of 4:1. This result is a pretty cool ratio, as it tells us that for every 4 times we get a useless card and miss our draw, 1 time will we get a useful card (a diamond) and complete our flush. Now all we need to do is put this figure to good use by comparing it to a similar ratio regarding the size of the bet that we are facing.
After you get your head around working out how many cards will help you and how many won't, the only tricky part is shortening a ratio like 38:9 down to something more manageable like 4:1. However, after you get used to pot odds you will just remember that things like flush draws are around 4:1 odds. To be honest, you won't even need to do this step the majority of the time, because there are very few ratios that you need to remember, so you can pick them off the top of your head and move on to step 2.
2] Compare the size of the bet to the size of the pot.
The title pretty much says it all here. Use your skills from the last step to work out a ratio for the size of the bet in comparison to the size of the pot. Just put the total pot size (our opponent's bet + the original pot) first in the ratio, and the bet size second. Here are a few quick examples for you...
- $20 bet into a $100 pot = 120:20 = 6:1
- $0.25 bet creating a total pot size of $1 = 1:0.25 = 4:1
- $40 bet creating a total pot size of $100 = 100:40 = 2.5:1
That should be enough to give you an idea of how to do the second step. In the interest of this example, I am going to say that our opponent (with a $200 stack) has bet $20 in to a $80 pot, giving us odds of 5:1 ($100:$20). This is going to come in very handy in the next step.
This odds calculation step is very simple, and the only tricky part is getting the big ratios down into more manageable ones. However, this gets a lot easier after a bit of practice, so there's no need to give up just yet if you're not fluent when it comes to working with ratios after the first 5 seconds. Give yourself a chance!
To speed up your pot odds calculations during play, try using the handy (and free) SPOC program.
3] Compare these two ratios.
Now then, we know how likely it is that we are going to complete our draw, and we have worked out our odds from the pot (pot odds, get it? It's just like magic I know.). All we have to do now is put these two ratios side to side and compare them...
- 5:1 pot odds
- 4:1 odds of completing our draw on the next card
The pot odds in this case are bigger than the odds of completing our draw, which means that we will be making more money in the long run for every time we hit according to these odds. Therefore we should CALL because we will win enough to make up for the times that we miss and lose our money.
If that doesn't make total sense, then just stick to these hard and fast rules if it makes things easier:
If your pot odds are bigger than your chances of hitting - CALL
If your pot odds are smaller than your chances of hitting - FOLD
So just think of bigger being better when it comes to pot odds. Furthermore, if you can remember back to the start of the article when we had the idea that calling smaller bets is better, you will be able to work out that small bets give you bigger pot odds - makes sense right? It really comes together quite beautifully after you get your head around it.
What if there are two cards to come?
In this article I have shown you how to work out pot odds for the next card only. However, when you are on the flop there are actually 2 cards to come, so shouldn't you work out the odds for improving to make the best hand over the next 2 cards instead of 1?
What Is A Flush Draw In Poker Room

No, actually.
Even if there are 2 cards to come (i.e. you're on the flop), you should still only work out the odds of improving your hand for the next card only.
The reason for this is that if you work using odds for improving over two cards, you need to assume that you won't be paying any more money on the turn to see the river. Seeing as you cannot be sure of this (it's quite unlikely in most cases), you should work out your pot odds for the turn and river individually. This will save you from paying more money than you should to complete your draw.
I discuss this important principle in a little more detail on my page about the rule of 2 and 4 for pot odds. It's also one of the mistakes poker players make when using odds.
Note: The only time you use odds for 2 cards to come combined is when your opponent in all-in on the flop. In almost every other case, you take it one card at a time.
Playing flush and straight draws overview.
I really tried hard to keep this article as short as possible, but then again I didn't want to make it vague and hazy so that you had no idea about what was going on. I'm hoping that after your first read-through that you will have a rough idea about how to work out when you should call or fold when on a flush or straight draw, but I am sure that it will take you another look over or two before it really starts to sink in. So I advise that you read over it again at least once.
The best way to get to grips with pot odds is to actually start working them out for yourself and trying them out in an actual game. It is all well and good reading about it and thinking that you know how to use them, but the true knowledge of pot odds comes from getting your hands dirty and putting your mind to work at the poker tables.

It honestly isn't that tough to use pot odds in your game, as it will take less than a session or two before you can use them comfortably during play. So trust me on this one, it is going to be well worth your while to spend a little time learning how to use pot odds, in return for always knowing whether to call or fold when you are on a draw. It will take a load off your mind and put more money in your pocket.
To help you out when it comes to your calculations, take a look at the article on simple pot odds. It should make it all a lot less daunting.
Go back to the sublime Texas Hold'em guide.
Can You Afford Not To Use
Poker Tracker 4?
What Is A Nut Flush Draw In Poker
“I wouldn’t play another session of online poker without it”
“I play $25NL, and in under 1 week PT4 had paid for itself”
What Is A Flush Draw In Poker Machines
Comments